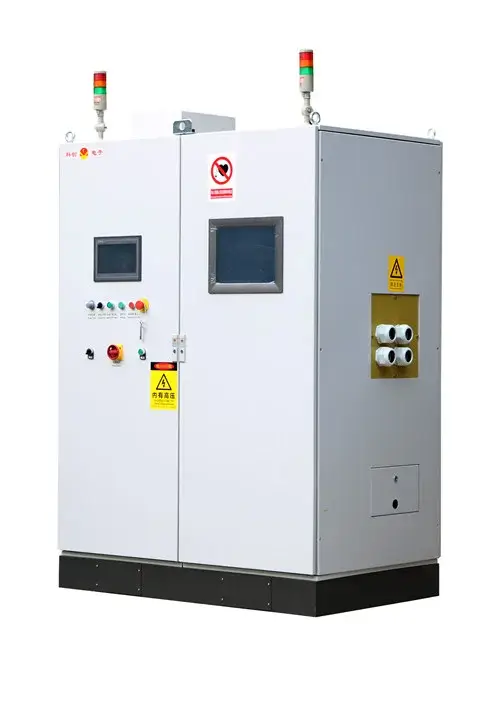
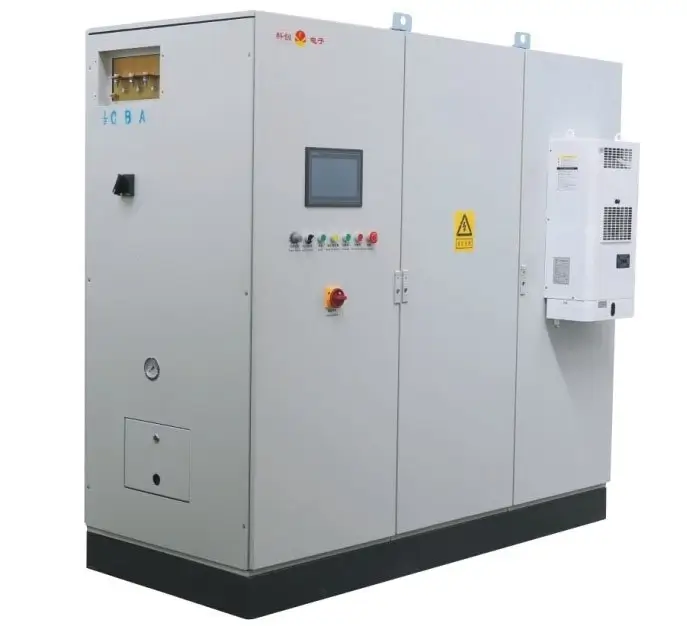
INDUCTION MELTING
Induction melting is a process that uses electromagnetic induction to melt materials. An alternating current in an induction coil creates a magnetic field, which induces eddy currents in the material placed within the coil. The resistance to these eddy currents generates heat, melting the material. It offers high efficiency, precise temperature control, and is environmentally friendly, being widely used in metal casting, recycling, alloy production, and the semiconductor industry.
Induction melting is a process used to melt metals and other materials using electromagnetic induction. Here is a comprehensive introduction:
Principle
- A high – frequency alternating current is passed through an induction coil. This generates a powerful alternating magnetic field within and around the coil.
- When a metal or other electrically conductive material is placed inside the induction coil, the alternating magnetic field induces eddy currents within the material. Due to the resistance of the material to the flow of these eddy currents, heat is generated. The heat produced is sufficient to raise the temperature of the material to its melting point, causing it to melt. Additionally, the magnetic field can also create a stirring effect on the molten material, which helps in achieving a more uniform temperature distribution and composition within the melt.
Equipment
- Induction furnace: This is the main equipment for induction melting. It consists of an induction coil, usually made of copper tubing, which is cooled by water to prevent overheating. The coil is surrounded by a refractory lining to contain the molten material and protect the coil from the high temperatures. There is also a power supply unit that provides the high – frequency alternating current to the induction coil.
- Control system: The control system is used to monitor and adjust various parameters of the induction melting process, such as the power input, frequency, and temperature. It ensures that the melting process is carried out accurately and safely, and allows for precise control of the melting rate and final temperature of the material.
Advantages
- High melting efficiency: Induction melting is highly efficient as the heat is generated directly within the material, resulting in rapid heating and melting. This reduces the melting time compared to some traditional melting methods, improving productivity.
- Good temperature control: It allows for precise control of the melting temperature. The control system can adjust the power and frequency of the induction current to maintain the desired temperature accurately, which is crucial for achieving consistent quality of the molten material.
- Clean and environmentally friendly: The process does not involve the use of open flames or combustion – related by – products, leading to less pollution. It produces fewer fumes and emissions compared to some other melting processes, making it more environmentally friendly and suitable for use in modern industrial settings.
- Versatility: Induction melting can be used to melt a wide variety of metals and alloys, including ferrous and non – ferrous metals. It is also suitable for melting small to large quantities of materials, making it adaptable to different production requirements.
Applications
- Metal casting: It is widely used in the metal casting industry to melt metals for producing various castings, such as automotive engine blocks, machinery parts, and art castings. The ability to precisely control the temperature and composition of the molten metal helps in producing high – quality castings with excellent mechanical properties.
- Recycling of metals: Induction melting is an important process in the recycling of metals. It can be used to melt scrap metals and separate different types of metals based on their melting points. This helps in recovering valuable metals and reducing waste.
- Production of alloys: In the production of alloys, induction melting allows for accurate mixing of different metals and additives. The stirring effect caused by the magnetic field helps in achieving a homogeneous alloy composition, which is essential for obtaining the desired properties of the alloy.
- Semiconductor industry: In the semiconductor industry, induction melting is used to melt and purify high – purity metals and alloys used in the production of semiconductor wafers and other electronic components. The precise temperature control and clean environment of the induction melting process are crucial for ensuring the quality of these high – tech materials.







